Table of Contents
Introduction
Blockchain system record information in such a way that it is challenging to hack, change or dodge the system.
Blockchain technology is multiplying, possessing a CAGR (Compound Annual Growth Rate) of 85.9%. With its help, we can boost transparency, trust, trackability, and security of the shared data between business networks and groups of individuals. Also, it plays a part to lowers data and security breaches.
In this blog post, we will discuss blockchain in detail. Discover what is blockchain and how does this technology works. Explore its decentralized nature, types, benefits, and disadvantages of technology, cryptographic concepts, and a variety of uses across industries.
Basic Concept of Blockchain

First, we have to understand two basic terms: Blockchain and bitcoin. Bitcoin is digital money or a coin, while blockchain is a technology that allows us to move from one individual to another digital currencies or assets. It’s essential to understand the fact that bitcoin is not a blockchain.
The main problem that blockchain can solve is money transfers. Today, if person X wants to transfer money to person Y from America to England, it is typically done using a third-trusted party. After taking some fee, that trusted party(say a bank) transferred the money to Y in England. This process usually takes some time.
Firstly with blockchain, we can transfer money without a trusted entity so that people can communicate directly. Secondly, we can do this process faster than traditional methods. Thirdly we can do it in a cheaper way than the fee that a third party collects.
What is blockchain in simple words?
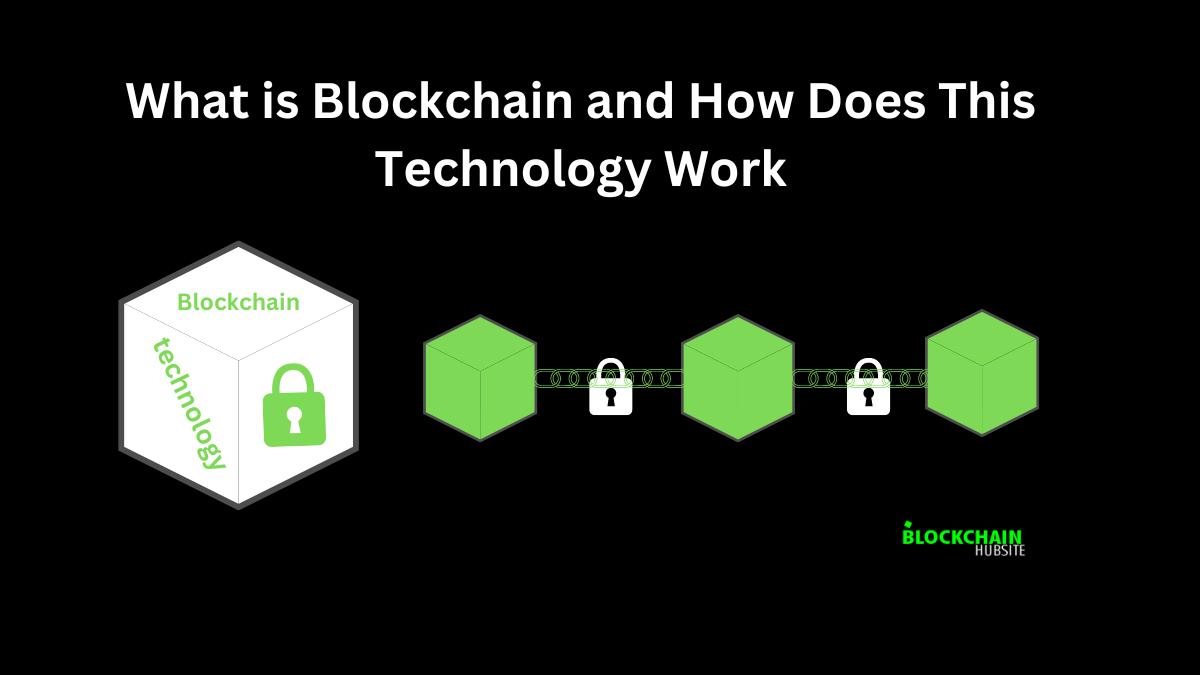
As the name suggests, it is a chain of blocks containing a distinct data type. The kind of data stored in these blocks depends on the blockchain type. Blockchain is considered open to the public distributed ledger. The concept of an open ledger is a chain of transactions that is open and public to everyone. It gives opportunity to everyone to own the network. Firstly, everyone can see where the money is and how much each has in their pocket. Secondly, everyone can decide whether a transaction is valid or not valid.
To authorize and facilitate transactions, it uses distributed peer-to-peer networks rather than the central management mechanism. To be accepted, all network participants must validate all the network nodes. After acceptance, the transaction adds to the chain and its data. That is why it is impossible to manipulate this distributed ledger technology.
How Does the Blockchain Technology Work

Over the last few years, various businesses have used blockchain technology because of the secure and transparent information stored in blocks. Ever wonder how it happens? It all happens due to the blocks themselves.
Instead of a lengthy string of records, information in a blockchain divides into secure blocks. Due to cryptography, it is impossible to alternate or replicate the data in the blocks. The question is, what do these blocks contain? There are specific data in each block.
For instance, If someone wants to sell a painting, the block should include the following information: the painting name, the new owner, the ex-owner, the transaction, and the sale time. In each block, there is an identifiable hash alongside the data. This hash represents a unique code that performs like a fingerprint. In the chain, the block contains the hash of the previous block—the hash changes automatically if any change occurs to one of the blocks. As a result, the consecutive blocks will disconnect from each other. It clearly shows data tampering, as the hashes don’t match each other.
As each chain distributes in a decentralized peer-to-peer network, it will increase the authenticity of the data. Everyone globally gets an exact copy of the hashes and chains on their computer. This way, the information is verified through the community in any blockchain. And hence we get a fully transparent distributed ledger.
History of Blockchain

An individual or group of people using the pseudonym(or name)” Satoshi Nakamoto” first introduced the concept of blockchain in 2008 on a white paper called “Bitcoin,” which is a peer-to-peer Electronic Cash System. Satoshi defined in this white paper a new electronic cash system with the help of which online payment could be transferred directly from one party to another without the requirement of a third party.
The files’ sizes containing all records and transactions on the bitcoin blockchain network continued to grow significantly. It reached 20 gigabytes in 2014, and finally, in early 2020 surpassed 200 gigabytes.
Blockchain Tecnology Market Size
The global blockchain technology market was valued at USD 5.7 billion in 2021 and is expected to grow to around USD 1,593.8 billion by 2030 at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 87.1% from 2022 to 2030.

Advantages
- One of the key features of this technology is Decentralization. One good thing is that no other instance is needed as an intermediary to authenticate transactions, reducing the validation time of transactions.
- Network distribution provides various benefits at the same time. One can own the network because different users have multiple copies of the same information. Also, because numerous network participants validate the data, practical inaccuracy is impossible.
- Due to its decentralized nature, it allows secure and quick validation of person-to-person transactions, eliminating the need for an intermediary and thus lowering the costs for users.
Disadvantages
- Execution of this technology can be time-consuming and costly.
- Users may experience delays and high fees once the users and number of transactions on it increase, which can slow the system.
- Maintaining the users’ privacy can be challenging because the ledger is transparent and public.
- At present, it has limited applications, such as cryptocurrency and transactions.
- The data stored on the blockchain could be more secure due to the lack of cybersecurity and regulation measures because the technology is still relatively new.
Types of Blockchain
Private and public are two primary types of blockchain, but several other variations like Consortium and Hybrid blockchains exist.
1. Public
These were the first to appear from various types of blockchains. The public blockchain allows anyone to join and conduct transactions because they are permissionless. Every user holds a ledger copy as it is an open variant. This way, anyone with internet access can become an authorized node.
The first public blockchains accessible to the common public included Bitcoin public blockchain. This type allows anyone who has internet access to conduct decentralized transactions
2. Private (or Managed)
In this type of blockchain, a single entity controls the whole network. Like public blockchains, it also performs on a peer-to-peer network decentrally. But who can be the node that only decides the primary authority? There is no need for the leading source to give equal rights to all users.
Contrary to public blockchains, where anyone having internet access can join the network, it remains restricted within a small company. Because the general access is in control, it is considered a partially decentralized network.
3. Hybrid
Hybrid blockchain is one of the different types of blockchain technology. It is a combination of both private and public blockchains. The significant applications of this type are in organizations that want to implement essential features from private and public blockchains.
In the hybrid blockchain, we typically keep records and transactions private, but we can declare them if needed by allowing access using the smart contract. Even though personal data stay protected within the network, it can still be verified. Private organizations can own hybrid blockchains, but they cannot change transactions.
4. Consortium
Consortium blockchains are like hybrid blockchains containing parts of both private and public blockchains. The only difference is that they are governed by many organizations instead of just one. Although it is difficult to set up these blockchains initially, once operated, these provide a high level of security. We consider consortium blockchains best for business as all the players in it must be hybrid and jointly responsible for blockchain.
Transaction Process of blockchains

The transaction process in a blockchain is the process of value transfer from one party(sender) to another(the recipient). This process involves the following steps:
1. The transaction process is initiated by the sender, who creates a message specifying the recipient’s address and transfers the amount of value.
2. The transaction is transmitted to the network, where the nodes confirm it. The nodes only verify the transaction if the sender already has the required balance and didn’t spend the transferred tokens.
3. The transaction is added to the blockchain as a new block once verified. Then the block is transmitted to the network and added to the existing chain of blocks.
4. The transaction is completed, and the recipient can obtain the transferred value.
What’s the Difference Between a Private and a Public Blockchain?

Key differences between public and private blockchains are the following:
- Accessibility:
The public blockchain is open, so anyone can participate in the network, see transactions and verify blocks. A private blockchain is restricted, so anyone who wants to access and participate in the network requires permission.
- Consensus
The network in public blockchain reaches consensus via a decentralized process, like proof-of-stake(e.g., Ethereum) or proof-of-work(e.g., Bitcoin). In comparison, this consensus process in private blockchain may be more centralized, including a limited number of nodes responsible for transaction validations and adding blocks to the chain.
- Transparency:
In a public blockchain, anyone can view transactions on the network. In comparison, administrators control the level of transparency in private blockchains.
In the first place, cryptocurrencies and decentralized applications used public blockchains. Private blockchains are used mostly in enterprise applications where the access requirement is small to a specific group of people.
- Performance:
Because of the decentralized and consensus process and the requirement to protect the network against malicious actors, the performance of public blockchains can be slower than private blockchains. Due to their centralized nature, private blockchains can provide faster transactions and higher scalability.
Promising Blockchain Use Cases And Killer Applications

1. Government Blockchain
In the following three ways, government blockchain can benefit governments worldwide.
1.1. Digital Voting
The voting process for elections can be done more securely and transparently with the help of this digital voting technology.
In this use case, we assign one specific ID to each vote, so creating a fake ID would be impossible. Votes can be counted immediately after the submission by government officials. That means, instead of waiting a few days in some cases, we can find out the outcome of an important election within an hour or two after the polls close. A great example of a start-up that uses this technology to ensure a transparent online voting platform is FollowMyVote.
1.2. Transparent Budgeting
The Corruption Perception Index provided by transparency.org shows that two-thirds of countries are highly corrupt. With the help of this technology, we can reduce corruption by making budgeting decisions in a government highly transparent.
1.3. Record Management
Birth and death dates, property transfers, marital status, and passports are individuals’ records maintained by national, state, and local governments. This recordkeeping of the data can be made more simplified and secure with blockchain technology.
2. Healthcare
In the healthcare industry, it takes more work for doctors and nurses to understand each patient’s history thoroughly. It’s because company databases where they put medical records are isolated.
Multiple healthcare companies, in real-time, can access the medical records share on a blockchain. Also, that data would stay secure.
3. Real Estate
Every five to seven years, average homeowner sell their houses. Blockchain would speed up these home sale processes by lessening paperwork and quickly confirming finance. Thanx for its transparency and encryption; it reduces fraud throughout the purchasing and selling.
4. Supply Chain Management

The real-time tracking of products can be made possible with blockchain technology while they pass through every stage and location of the supply chain. A decentralized database allows multiple parties, customers, suppliers, and retailers to access this data.
5. Finance
In finance, we can use blockchain in a couple of ways.
For investment and trade, blockchain can help by
a. improving transparency of governance
b. Improving the speed of transfers
c. Decreasing capital requirements
d. And reduce the possibility of fraud and human inaccuracy
In the case of international transfers, blockchain can aid by reducing the cost of these transfers by dropping the requirement of banks for manual settlement of transactions.
6. Smart contracts
Smart contract creation and implementation can be done conveniently with blockchain. These are automated contracts between buyer and seller where the terms of conditions are written directly into lines of code.
Proof of Work (PoW) VS. Proof of Stake (PoS)

Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS) are two different consensus mechanisms used by blockchain networks to agree on the state of the ledger.
In PoW, to create a new block and earn a reward, miners compete to solve a computationally difficult puzzle. This is referred to as mining. The idea is that the miner who solves the puzzle first gets to add a new block to the blockchain and earn the reward.
In PoS, instead of mining, validators are chosen to create new blocks based on the number of coins they own and are willing to “stake,” or lock up as security. This is referred to as staking. The idea is that the validator with the most stake has the greatest chance of being chosen to create a new block.
Blockchain VS SWIFT System
Blockchain is a decentralized, distributed ledger technology, while the SWIFT(Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication system) is a centralized network. In the case of blockchain, we depend on miners; on the other hand, we rely on financial institutions in the case of SWIFT.
Blockchain VS Bitcoin

- Blockchain is distributed decentralized database, while bitcoin is a digital currency.
- The primary purpose of blockchain is to produce cheap, safe, and secure circumstances for peer-to-peer transactions. The main aim of bitcoin is to secure and improve transaction speed by avoiding government restrictions.
- With the help of blockchain, we can quickly transfer anything to property rights of stock from currencies, while bitcoin as a currency is limited to trading.
- Because of showing flexibility to changes, blockchain can serve different industries while, on the other hand, bitcoin is comparatively less flexible.
How to Invest in Blockchain?

There are various methods to invest in blockchain technology:
1. Buy Cryptocurrency
Buying a cryptocurrency like Ethereum or Bitcoin is one of the ways of investing in blockchain. We can buy and sell these cryptocurrencies on cryptocurrency exchanges, and their value depends on the supply and demand in the market.
2. Invest in Blockchain Companies
We can invest in blockchain in another way by investing in companies using this technology. We can use blockchain in these companies to develop blockchain-based new products or services or enhance current businesses’ performance.
3. Invest in Bockchain Funds
We can also invest in investment funds that concentrate on blockchain-related companies. In these funds, investors can invest in diversified blockchain stocks.
4. Participate in Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs)
Specific blockchain projects through initial coin offerings(ICOS) raise money, allowing investors to purchase tokens in exchange for an investment. It is vital to research before participating in ICOs because they can be risky and not regulated.
Note: It is essential to do your own research and due diligence before making any decisions regarding investments in blockchain because it carries inherent risks.
Is Blockchain Secure?

Blockchain technology ensures trust and peer-to-peer security by several different means. New blocks are initially always stored in a linear and chronological order. In fact, at the end of the blockchain, they are added continuously. One can change the block’s content in the blockchain only with the approval of most network participants. It’s all because there is a hash and the relevant date in each block that came before it.
Suppose a hacker manages a blockchain node and wants to take everyone else’s bitcoin by changing a blockchain. The copies made by everyone else wouldn’t match their document if they tried to change it. This kind of hack could be successful only if the hacker makes their new copy a majority copy and thus a legit chain by simultaneously possessing and changing 51% of the blockchain copies. Because of the change in each block’s timestamps and hash codes, a hacker has to rewrite them, making such an attack very time-consuming and costly.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology is a decentralized, distributed database that allows the secure recording of data and the creation of a digital ledger of transactions. Rather than a single central authority, it is a recordkeeping system based on a network of computers.
Blockchain technology provides several benefits, including increased security, transparency, and reduced need for intermediaries. It has the potential to revolutionize a wide range of industries and applications, and we are already using it in areas like finance, supply chain management, and voting system.
Blockchain also has its limitations and challenges, like any new technology though. The issues like regulation and scalability still need to be fixed as the technology is in the early stages of development. However, despite these challenges, the potential of blockchain technology is unquestionable, and it is likely to continue to play a vital role in the future of technology and business.
FAQs
1. Who created blockchain?
Satoshi Nakamoto created blockchain in 2008; ever since we have been using blockchain to develop from cryptocurrency wallets to smart contracts and various other applications.
2. Why is blockchain popular?
A transparent and immutable way of storing and exchanging data makes blockchain popular. Also, this technology is becoming increasingly popular because of its use in developing cryptocurrencies like bitcoin.
3. Why is blockchain the future?
Blockchain technology is transforming how we use, store, and access data. From security to transferring data, it solves many problems these days. Also, by using this technology, the hacking or tampering of data is almost impossible.
4. Who controls the blockchain?
Rather than a single entity, all the users who interact with it control the blockchain.
5. Where is blockchain used in real life?
Blockchain is being used in a wide range of real-world
applications. Asset management, cross-border payments, healthcare, cryptocurrency, birth and death certificates, contract management, and money transfer and payment processing are some of the most popular real-world applications of blockchain technology.
6. Will blockchain replace cash?
It is unlikely that blockchain technology will replace cash any time soon, despite the technology’s potential. It is hard to say whether blockchain technology will replace some money because it is still in its early stage and hasn’t been thoroughly tested in a large-scale environment.
7. Will blockchain destroy banks?
It is unlikely that blockchain technology will completely replace banks. Banks provide services beyond traditional financial transactions, such as loan and insurance services, which blockchain technology cannot supplement. Therefore, rather than replacing existing banking services, blockchain technology will likely support and improve them.
8. Can we use blockchain without cryptocurrency?
Yes, blockchain can be used without cryptocurrencies. An example is private blockchains, where only specific entities can access and use the data. Furthermore, blockchain technology can maintain and manage data without using cryptocurrencies, such as supply chain records or digital asset ownership.