Table of Contents
Introduction
Blockchain technology is becoming more important in everyday life as it helps people save time and money. Due to food chain fraud and consumer concerns about food quality and safety, food safety is becoming more significant. According to the WHO, one in ten people gets sick from food, and 2 million die from contaminated water and food. People no longer trust general store food and information.
People no longer trust the food items and their information at general shops. Instead, they want to know that what they buy comes from reliable sources and that the item information hasn’t been changed or isn’t clear. It’s difficult for consumers to buy food from afar because of concerns about contamination and spoilage.
A company’s reputation is more important than anything else in long-distance business relationships. Blockchain makes this possible without the need for a trusted third party and with an added layer of safety because no information is ever deleted from the chain of custody for a given item of food or transaction. Companies care a lot about their image and want to ensure everything runs smoothly regarding food.
Using IoT in FSC has allowed for real-time tracking, data capture, and data transfer, while blockchain technology gives better reliability, product/service security, and traceability. The integration of IoT and blockchain would enable data security, trust, visibility, dependability, and real-time information-sharing facilities in FSC.
This article discusses how blockchain and IoT are changing the food supply chain in various ways, such as improved traceability, quality assurance, food safety management, and supply chain optimization. By using these technologies, the industry is making big steps toward ensuring food is safe, improving efficiency, and building trust between producers, suppliers, retailers, and customers.
Understanding the Food Supply Chain
Food supply chains, also known as “farm to fork,” include the sourcing, processing, handling, distribution, and sale of foodstuffs (i.e. raw materials) and the management and documentation of these activities from beginning to end.
Managing food supply chains requires documentation of numerous criteria, such as the quality of raw materials, processing methods, storage conditions, final product quality, and more. This information must be synchronised and shared among all parties along the supply chain to ensure customer safety, regulatory compliance, product consistency and quality management, and ultimately, customer satisfaction.
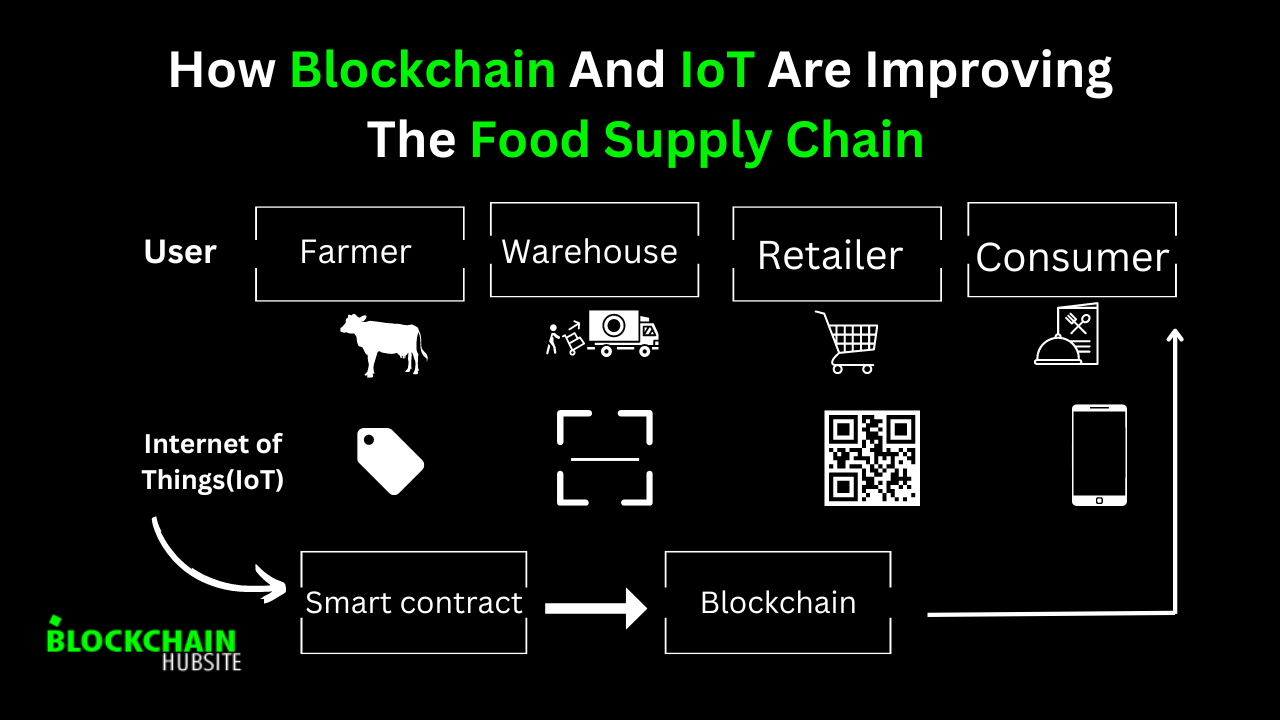
The food supply chain simplified
Please take a look at this simplified food supply chain to get an understanding of the many players and their responsibilities.
1. A farmer grows wheat and collects it.
2. A machine grinds the wheat into flour
3. The flour goes to a food manufacturer, which mixes ingredients from other processors to make cereals, bread, pasta, and other food items.
4. The food products are sent to a distributor, who handles the logistics and transport of the goods to different retailers.
5. Retailers then sell the food items to end-users.
Role of Blockchain in the Food Supply Chain

Each year, one-third of the food that is produced on a global scale is either lost or wasted. Loss occurs throughout the supply chain, beginning with production and harvesting and continuing through processing and delivery.
Additionally, greenhouse gases are produced during food manufacturing and delivery, with wasted food alone accounting for 8% of the world’s total greenhouse gas emissions.
Also, most ‘lost’ food is thrown out because of its appearance. Because of tight cosmetic requirements, grocery stores in the United States and Europe sometimes reject perfectly edible vegetables. Better management of food supply chains is the solution to food waste. To solve this problem, we’ll need a solution that takes a straightforward approach.
The agricultural supply chain currently needs more traceability and transparency, but blockchain has the potential to greatly improve the situation.
Blockchain technology can store Supply chain transactions in an immutable and trustworthy database.
Think about being able to follow the locations of products in real-time and receive updates on their progress at certain intervals.
The origin and safety of food products can be verified using blockchain technology.
By utilizing blockchain technology, consumers and producers will have greater confidence in the food supply chain. According to IBM’s research, 71% of consumers who consider traceability vital are willing to pay more for brands offering it.
The supply chain can be streamlined and automated with the help of blockchain technology. For example, bills of lading can be made electronically and smart contracts can be used to ensure acceptance. If government officials and businesses could agree on some standards, more food would make it to tables where it might be eaten.
Smart contracts can also help reduce paper usage. We have seen a net increase in paper use and filing over the previous two decades. Cloud computing and email are needed to modernize the agri-supply chain.
Imagine a system with no fees or paperwork involved in processing documents, accepting cargo, clearing for export, or settling payment. This is a workable solution.
Then there’s the world of digital markets built on their blockchains. This is where competitive pricing and offers come together from several different service providers. Meanwhile, Internet of Things (IoT) trackers will sort out food fraud and waste by connecting producers with final buyers.
Role of IoT in the Food Supply Chain

Consider this: businesses providing food services might benefit from reduced food waste and more adaptable produce inventories. Profitability requires meeting the growing demand for processed foods without compromising hygiene standards. The operations dynamic is to keep the food quality up while reducing costs.
The Internet of Things (IoT) and big data analytics can help food service businesses integrate their supply chain and increase efficiency in packaging, warehousing, and logistics to meet the demands of the on-demand distribution of massive volumes of products across diverse categories. While real-time asset tracking and mobile workforce management solutions increase efficiency and streamline operations, they do nothing to improve service levels or decrease order lead times in complex shipping workflows.
Internet of Things (IoT) supply chain management technologies gather valuable data from inside and outside the company to improve asset utilization and customer value. Additionally, contextual intelligence is available in an IoT-enabled supply chain. Analytical models leverage big data to estimate demand for a specific time of day, recommend product pairing to avoid multiple orders, assess how many drivers are needed in a shift, and arrange inbound and outbound cars to minimize truck rolls. Reducing a delivery truck’s stay periods by even a few minutes results in significant savings for the entire fleet.
In many ways, an IoT ecosystem can streamline a company’s operations. It streamlines the processes of asset control, legal conformity, and product/asset reconciliation. It also deals with the issue of hidden fees connected to loading tools and reusable containers. Warehouse inventory and material handling expenses can be reduced through predictive maintenance for trucks, forklifts, and conveyors and timely repairs and maintenance of returnable containers, racks, and pallets.
IoT-powered logistics solutions guarantee the safety of the cold chain. It automatically modifies individual networked systems to prevent dangerously high or low humidity and temperature in storage facilities and transport vehicles. Data generated by devices provides audit trails in real-time for food safety professionals and aids in cold chain analysis for supply chain planners.
The self-sustaining reaction is made possible across warehousing and logistics processes because of IoT devices’ ability to communicate with one another and with business systems. The smart bins that automatically restock supplies, the drones that perform stock checks, the autonomous vehicles that plan loads and schedule routes without human intervention, the intelligent storage racks that monitor the quality of produce and expiration dates, and the robots with a 3D vision that remove wilted greens from the shelves all rely on a unified data-sharing framework.
Things are looking up for the food service industry. Food services businesses will benefit greatly from the Internet of Things and big data analytics.
Integration of Blockchain and IoT in the Food Supply Chain
Together, blockchain technology and Internet of Things (IoT) sensors have the potential to increase freshness, quality, and safety throughout the fresh food supply chain, boosting industry margins on consumable goods by as much as 50 percent. Moreover, the transparency provided by the blockchain system would allow businesses to earn their customers’ trust and boost their brand value.
The ideal Traceable Food Supply Chain system aims to
- Keep food safe and in good condition
- Adequate communication among all parties involved
- Reduce supply chain costs to make food more affordable
- Inventory tracking and management in warehouses and stores
How does it work?
All product details are now safely kept in the cloud thanks to blockchain. The transaction log is updated in the blockchain whenever it reaches a new intermediary to the consumer.
QR codes and near-field communication (NFC) chips store this data. At each stop, a QR code on the product is scanned to record the time and location that the goods were there. A customer can quickly check if a product is real before buying it by reading its QR code or NFC chip. To see this, a client only needs a smartphone and internet access. A ledger is used to record the data gathered here. The consumer has never before experienced this level of transparency.
But where does IoT come into play?
When a product is equipped with a QR code or Near Field Communication chip, its location and movement can be traced.
The Internet of Things becomes apparent when many sensors monitor a product’s vital information in real-time. About half a million people die yearly from food-related illnesses, making this issue even more pressing. Certain temperatures must be maintained to prevent food from spoiling. Sensors, such as temperature sensors, are placed at various checkpoints, and when a food supply passes through them, the data is recorded and added to the blockchain.
Immediately upon discovering any signs of rotting, the product is sent back to the maker. It keeps people from getting spoiled deliveries, which saves a lot of time, money, and fuel and puts the consumer’s health at risk. This causes significant financial losses for many companies.
Having a spoiled product in the hands of consumers still harms the company’s image. A customer’s trust in a brand can be damaged with just one low-quality purchase. Walmart and IBM collaborate on blockchain technology to expand its application across all industries.
Case studies and real-world examples
Sawtooth: A New Approach to Seafood Traceability: Sawtooth documents the journey of seafood from the ocean to the table, bridging the gap between the digital and physical worlds. Any object, like the fish in this scenario, can have an Internet of Things sensor attached to it to monitor its position, temperature, humidity, motion, shock, and tilt. At the same time, it is in the care of another person. The final buyer has access to reliable, comprehensive documentation.
Walmart and IBM Food Trust: Walmart and IBM worked to set up a blockchain-based system for tracking and tracing food items in its supply chain. IoT devices and blockchain technology made it easier to track down the source of goods like mangoes and pork. It now takes seconds, not weeks, to find out where contaminated food came from.
Pros and Cons of Blockchain with IoT in Food Supply Chain
| Blockchain/IoT Pros | Blockchain/IoT Cons |
Most of the time, the blockchain is used in places where there is a problem with trust, such as store networks. This framework is currently set up to support a simple store network. | When blockchain and the Internet of Things (IoT) are combined, the cost of RIFD (radio frequency identification) tags is very high compared to other recording systems, such as barcodes and QR codes. |
| There is less need for human labour because everything is now automated. | Many of us need to learn more about blockchain technology, so it will be even harder for regular people to understand when combined with IoT. |
Since the product’s expiration date and the retailer’s shipping information are clearly shown, you’ll always know whether your order has arrived. | Many good companies can only add this technology to their system if it’s cheaper. |
| Because RFID tags are used, the information is encrypted, and each item is given a unique RFID tag ID. This ensures that no one can access the data and keeps the data safe. | |
| In every framework, there will be a third ordinary person who will serve as power. Because of this, the framework is also centralized. The outsider contribution will not be taken into consideration. With this blockchain technology, everyone is treated the same way, so permitting them to do something carefully is impossible. |
Conclusion
Integrating blockchain and IoT technologies in the food supply chain improves traceability, enhances quality control, and enables efficient supply chain management. These advancements contribute to increased transparency, reduced fraud, and improve overall food safety, leading to a more secure and reliable food system for consumers.
FAQs
1. How can blockchain improve the food supply chain?
Blockchain can improve the food supply chain by increasing transparency, traceability, and efficiency through secure and unchangeable record-keeping, lowering fraud, ensuring food is safe, and allowing for better inventory management.
2. How can IoT improve the supply chain?
With the help of IoT, businesses can see the location of their products and assets at any point in the production and distribution processes. This visibility can help businesses manage their inventory better, speed up delivery times, and lower the risk of losing or damaging products.
3. What is an example of IoT in the supply chain?
One example of IoT in the supply chain is using smart sensors to track real-time inventory amounts and conditions.
4. What are the benefits of blockchain for food traceability?
There are many ways in which blockchain technology might improve food traceability. These include increased data accuracy and dependability; decreased data fragmentation and complexity; increased data visibility and accessibility; and increased data ownership and management.
5. What value does blockchain bring to the imported fresh food supply chain?
The blockchain adds value to the fresh food supply chain by making it more transparent, traceable, and trustworthy through permanent records. This makes it possible for stakeholders to check the products’ origin, quality, and safety.
6. How can blockchain solve hunger?
Blockchain databases are transparent and immutable, so a government that donates $10 million to food aid for refugees in a certain region can see where every cent goes.
7. How does blockchain improve sustainability?
Blockchain technology opens up new ways to improve sustainable efforts by making tracking and confirming emissions easier. Companies can be held accountable for their sustainability claims since their carbon balances and other environmental metrics can be tracked transparently and immutable.
8. What problems can blockchain solve in the supply chain?
Blockchain technology can greatly improve supply chains by simplifying and speeding up procedures such as product delivery, tracking, and communication among business partners and providing faster access to funding.
9. How does blockchain lower supply chain costs?
Since blockchain permits real-time product tracking within the supply chain without intermediaries, the expense of transporting goods can be minimized. Removing intermediaries can save money, stop counterfeits or scams, and make the same product less likely to be made twice.
10. What does the future hold for supply chain blockchain?
Brands could improve their corporate image if they provided more information about how their items were made. Blockchain could also improve its reputation and win the public’s trust through open access to supply chain data.