Table of Contents
The increased Internet and digital money usage by the common people has encouraged several studies to investigate their performance and uses. The success of the blockchain is demonstrated by the improved security, transparency, and cost-efficiency of various transactions occurring in real life.
Businesses have been focusing a lot of their efforts recently on the idea of digital transformation. Firms must undergo a comprehensive digital transformation of their people, business, and technological aspects to deliver more effective and efficient services. As a result, blockchain, a disruptive technology, is critical to assuring enterprise digital transformation.
This article will discuss how blockchain accelerates digital transformation and the future for firms that use it.
Blockchain Technology and Digital Transformation
Blockchain technology is a way to build trust without a central authority, using mathematics and cryptology ideas. The blockchain structure is like a computer network, with computer owners as the main building blocks. Because of this, blockchain is seen as a big step forward in decentralized information technology.
There are three kinds of systems: centralized, decentralized, and distributed.

Blockchain technology is used in distributed networks without a central authority. With its distributed nature, blockchain technology will help digital transformation.
On the other hand, digital transformation uses technology to create new business models, processes, and systems that are more competitive and efficient.
Most of the research found a connection between digital transformation and changes in business and organization. For instance, Matt et al. described digital transformation strategy as a blueprint that supports companies in governing the transformations that arise owing to the integration of digital technologies and their operations after a transformation.
The Importance of Digital Transformation

Technology is enhancing people’s lives and making work easier in many fields. One of the keys to a company’s continued success in the face of the future is its ability to undergo a digital transformation and meet the changing needs of its customers. It improves businesses’ ability to compete in an economy that shifts continually in reaction to technological developments. Companies can get operational and productive benefits from a digital transformation if they handle it properly.
Our post-pandemic world is evolving into a technological state of mind. Successful companies will create smart experiences and customer journeys that improve people’s lives. Companies that don’t try to take advantage of new AI technologies and don’t use data to predict demand trends and make decisions that improve the workforce will fail.
Blockchain is a key player in digital transformation

Businesses are among the first to recognize blockchain’s potential applications outside of the cryptocurrency space. Tanla Platforms, based in India, released a new communications platform-as-a-service with Microsoft last year that was blockchain-enabled and built on Microsoft Azure.
Some people have used blockchain to support parts of enterprise content management systems. It can authenticate records and give an audit trail of permitted interactions when implemented properly. Still, it can manage material differently than a content management system does.
According to Ivan Kot, a consultant at Itransition, a Denver-based software development firm, technology is already a crucial aspect of many companies’ digital transformation strategies. This was back in January of last year. He predicted that other sectors would follow the financial sector’s lead in adopting blockchain technology as large-scale projects revolutionized the sector.
Even while blockchain is getting close to becoming popular, its lack of development in the digital workplace is the only thing that seems surprising. Remember that in 2008, a person or group named Satoshi Nakamoto came up with the idea for the first decentralized blockchain. The technology and the frequently disorganized approach in which organizations have implemented digital transformation initiatives provide historical and technological explanations for poor adoption.
But that’s beginning to alter.
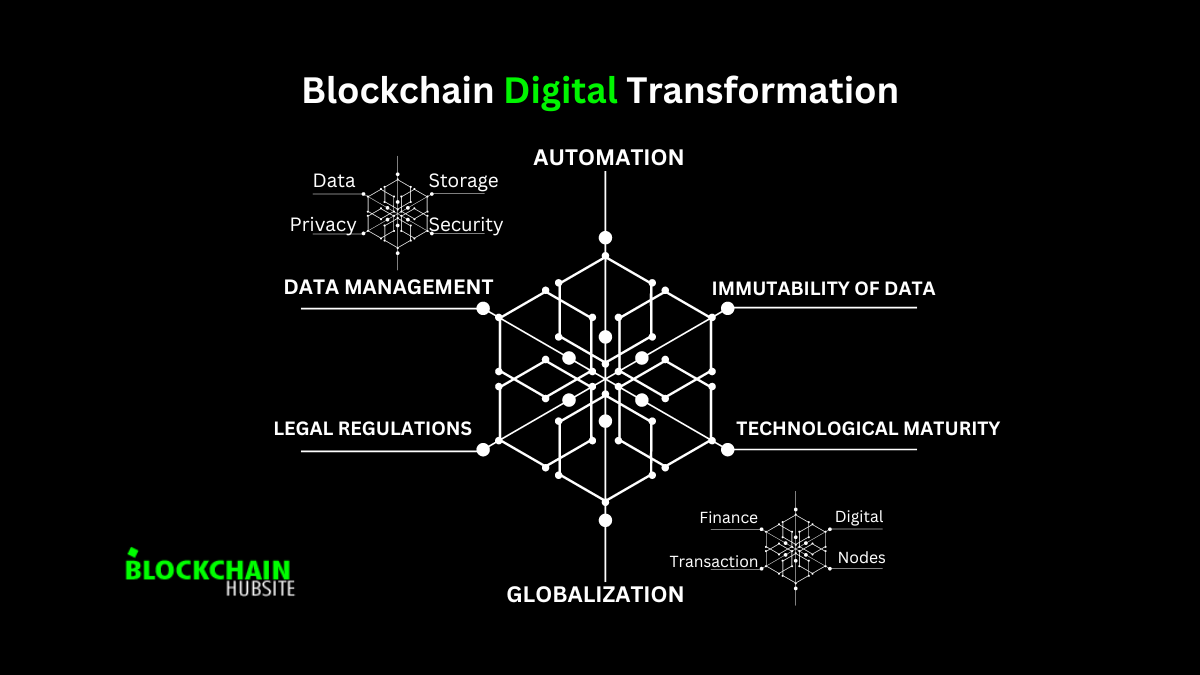
Blockchain Technology Advantages in Digital Transformation

While blockchain technology is essential to ensure the digital transformation of businesses, it also offers some benefits and solutions. The benefits of blockchain technology include the following:
1. Processes Optimization And Integration With Other Technologies
Blockchain helps businesses cut down on transaction fees, eliminate intermediaries, and streamline data collection, editing, and distribution, all of which are areas where researchers have been focusing their attention. According to Kopyto et al., adopters can get a competitive advantage by driving digital transformation through blockchain integration with other technologies.
Businesses with robust IT departments may develop blockchain solutions, eliminating their need to rely on external providers. By working together, TMS (Transportation Management System) and blockchain can make switching service and product providers more difficult, for instance. Maersk and IBM’s TradeLens effort is a real-world application of blockchain technology to the supply chain, ERP, and warehouse management processes.
Norström and Lindman talked about a prototype implementation of blockchain technology in municipal use cases, which helped cut costs by automating previously laborious processes and preventing citizens from double-using coupons. In addition, digital identity systems built on the blockchain can be utilized to boost the performance of digital services. There is a significant danger with user credential authorization and data management inside a decentralized control system when one-stop services are used without a competent identity management system. New business models for companies and society can be developed by combining blockchain with innovative technologies such as AI, the Internet of Things, and machine learning. Hence, combining blockchain with other technologies can improve service delivery.
Some research has even concentrated on blockchain’s potential to enhance data organization. The decentralized nature of blockchain technology makes data more transparent because it is accessible to all participants in the network. The information is also protected and organized chronologically. Many operations benefit from this, including auditing, reporting, and data analysis.
2. Automation
The primary goal of process optimization is to maximize efficiency while cutting expenses. The business climate in countries with advanced economies has the sufficient technological and organizational infrastructure, making them ideal for blockchain implementation.
When certain criteria are met, collaborative networks with many different participants can operate in a highly automated manner, and smart contacts are the facilitators that help keep transactions between many different parties secure and immutable. Several experts agree that smart contacts play a crucial part in the automation process, citing their potential applications in instant tracking, product authenticity, peer-to-peer communication, opportunistic prevention, and payments between participants.
With minimal loss of productivity, automating processes using blockchain technology can mitigate risks associated with politics, personnel, economics, and regulations. Because everyone involved has constant access to data and real-time updates regarding all processes, everyone can make necessary adjustments and keep everything under control. As a result, blockchain technologies can streamline and integrate various business processes, allowing companies to operate more effectively.
3. Immutability Of Data
Many studies have shown that blockchain technology offers a novel and encouraging method of resolving data security issues. In this context, blockchain technology provides a reliable, decentralized platform for storing and sharing information. The technology allows for secure data exchange by combining private and public blockchains. It may be used to securely monitor and document entire processes and provide secure asset sharing, data tracking, and strong peer-to-peer communication, among other applications.
Keyless Signature Infrastructure (KSI), developed by Guardtime, is a blockchain-based system that employs hash-based encryption and digital signature-based authentication to guarantee security and scalability, as described by Andoni et al.
In addition to resolving the data management issue, blockchain usage prevents the data and transaction log from being readily tampered with by documenting all processes in the network. The immutability of blockchain data assures that it cannot be altered or deleted, which is very important in municipal applications such as voting. Mattke et al. provided yet another illustration. The “MediLedger project” is an ecosystem built on the blockchain to track the entire drug production and distribution process. Product verification and tracking, IP protection, and counterfeit prevention are just a few of the many uses for this system.
Experts determined, based on evidence, that blockchain technology needs to develop further before its full potential in data protection can be achieved and that if customers are confident of the immutability of their data, security and safety barriers between a company and a client are more likely to vanish.
4. Transparent Intra And Inter-Organizational Collaboration
Some research has shown that utilizing a blockchain can improve the transparency of both internal and external business partnerships. Companies have their internal processes, and in large organizations, this can lead to serious disruptions if the various departments are properly linked. Since blockchain promotes trustworthiness, facilitates organized recordkeeping, and enhances communication, the experts claim that technology can be used to address the issue of information asymmetry.
Supply chains (which include manufacturers, logistic providers, retailers, and so on) are incredibly complicated systems that necessitate close cooperation between many different entities.
Companies are interested in blockchain-based applications and cross-industry collaboration for various reasons, including the opportunity to gain the benefits of new technologies (such as cost savings, transparency, and decentralization), expand their customer bases, and mitigate risks to their bottom line. The blockchain also removes barriers between large and small businesses, allowing them to connect and the wider world. Yet, businesses are considering implementing blockchain after learning about the technology and seeing its potential benefits.
5. Globalization
As the rate of digitization grows internationally, it is critical to preserve transparent interaction among various entities such as individuals, businesses, and governments. Another reason for blockchain adoption is the geographical growth of business networks and the rising demand for data transparency, safety, and accountability.
Global collaboration has a big impact on many different areas, and with blockchain and cryptocurrencies, delays in global collaboration can be avoided. Due to the decentralized nature of blockchain, nodes can be established anywhere, join the network, and communicate with the other participants effortlessly. Therefore, globalization raises organizations’ competitiveness and vulnerability in the global market.
In this way, blockchain technology might make it easier to share information clearly and quickly and adapt to a fast-changing environment or act ahead of it. In addition, such an attempt might provide a new financial system for a cashless world free of service, providing borders and intermediaries. In simpler terms, this means that data transmission may be handled more quickly and freely across borders without the influence of local legislation and authorities, thanks to the immutable ledger, decentralization, and peer-to-peer transactions enabled by blockchain technology.
Blockchain Technology Implementation Challenges and Steps for Businesses
Blockchain-based digital transformation challenges are linked to various concerns that can be considered paradoxical conflicts. Competing goals, values, and attitudes cause these conflicts. There are also challenges with blockchain deployment, security, education, and regulation.
Here are some of the challenges.
1. Legal Regulations

The financial uses of blockchain have been the primary attention of financial regulators worldwide. There are no globally accepted rules for applications that use blockchain or smart contracts, but there are no legal frameworks for blockchain-based applications. Legal laws and government support are essential to boost user trust and acceptance of blockchain-based applications. Therefore, bridging the gap between regulatory compliance and blockchain-based application development could facilitate favourable market interaction and accelerate blockchain innovation.
Jensen et al. say that the need for unified standards and regulations makes it hard for some governments and businesses to justify the cost of setting up technology. Canada and Saudi Arabia were the first to sign an official agreement with TradeLens in 2019, followed by the Netherlands, Singapore, and Kuwait.
However, more work must be done before it can be used globally.
For major corporations to actively work on blockchain-based applications, authorities worldwide must recognize the significance of blockchain technology in digital transformation.
Another challenge for decentralized platforms is the need to follow privacy requirements. For example, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) of the European Union mandates that all companies must take reasonable steps to protect their users’ personal information. Governments can use labels (a symbol that the platform has basic support) to back blockchain initiatives and increase user trust.
Wealthy nations like the United Kingdom publicly support blockchain by funding digital economy research centres. Although the greatest risks are related to public or hybrid blockchains, the simplest and most practical solutions soon are private and consortium blockchains with limited users.
2. Data Management

Before implementing blockchain technology, it is important to address the many issues concerning data management. The reduced scalability of blockchain technology has led some experts to argue that it cannot replace conventional databases.
The scalability of the network is decreased because a rise in the size of the network and the volume of data causes transactions to take longer and cost more money.
Public blockchains frequently experience this issue, but private systems have less traffic and are easier to control.
Another area for improvement is the storage and flexibility of data. Decentralization is an advantage since blockchain is a distributed network, but it increases storage resource requirements for all participants. Hence, a large amount of data in a constantly developing network multiplies operations, increasing costs due to a need for economies of scale. Data immutability creates problems when incorrect or outdated information needs to be changed, according to Liang et al.
Finally, data conversion to digital format is a restriction. While blockchain technology can reduce administrative burdens like paperwork, time spent transferring information, and manipulated data, the authenticity of data inputs cannot be guaranteed. Important criteria include data input standards, privacy, clarity, and correctness. To effectively manage data, it is necessary to meet all of these criteria.
3. Technological Maturity

Technological development can be evaluated by how well it adapts to new circumstances and meets its end users’ needs. Each technology’s outcome is unpredictable, and blockchain doubts represent this unpredictability.
While interest in blockchain has risen, extensive technical analysis has little empirical evidence, and existing conclusions should be double-tested in multiple fields. This is primarily because the technology is still in its infancy and needs to be mature enough for worldwide acceptance in numerous sectors, and further study is necessary.
4. Security And Privacy

The level of trust that individuals and businesses have in the blockchain depends heavily on its ability to keep their data private and secure. The consensus algorithm is the root of the first problem. Theoretically, public blockchains offer a high level of security, with the likelihood of an attack depending on the strengths of honest miners and potential attackers. Nevertheless, the PoW consensus method has flaws, leading to a 51% attack if a person controls more than half of the network. Other consensus algorithms, such as PoA, PoS, or PoET, should be investigated to assure security and performance.
While the basic security aspects of the blockchain (such as anonymity, immutability, and distributed control) promise to improve data sharing, Klöckner et al. note that there are still some unknown variables.
Based on blockchain breach reports from 2011 to 2018, there are still some technological vulnerabilities to external threats (e.g., transparency gives a chance to discover flows in a blockchain-based applications code, risk of losing private keys, complexity in the urgent system shutdown, etc.), which may discourage potential users from adopting blockchain. Wan et al. noted that smart contracts are another blockchain technology barrier, and some solutions have security flaws and cause further delays.
For this reason, current smart contracts are more vulnerable to cyberattacks than older forms of software. Also, Supranee and Rotchanakitumnuai talked about how a lack of trust among stakeholders and the potential for sensitive data to fall into the wrong hands could be barriers to wider blockchain adoption, especially in public situations. Because of this, private and consortium solutions are now the best option.
Privacy concerns are greater among potential consumers who are aware of the blockchain’s potential and have higher expectations.
Hence, privacy is crucial, users are hesitant to disclose private information with third parties, and more information regarding risk mitigation options (such as restricting access to data to only the intended parties, actively managing the trust, minimizing fraud possibilities, etc.) is needed.
5. Integration And Implementation

Many researchers have analyzed the difficulties of integrating blockchain technology into existing systems. The importance of supporting infrastructure and complementary solutions (such as the Internet of Things, scanners, and RFID) has been emphasized by several researchers, including Gruchmann and Bischoff and Sternberg et al. Major actors may need help with such initiatives since they need big changes and investments.
Although the long-term benefits are enormous, perceived complexity limits acceptance and implementation in many application domains. Unfortunately, there has yet to be a lot of scientific research done in this area. Those obstacles need to be tested more by large multinational corporations and small and medium-sized businesses.
6. Readiness Level
According to Arefjevs et al., the debate over whether or not to adopt new technologies is at the heart of the ongoing digital transformation process. This debate centres on topics like the importance of an organization’s culture and the competence of its employees, the relevance of existing technologies, the level of support they receive from the government, and so on.
In the case of blockchain, many people who want to use it need more knowledge, experience, or even a basic understanding of when and how it can be used. When the benefits of implementing blockchain technology are within the hazards, Yang, Liang, and fellow researchers believe senior management authorities may be less excited about the technology. Consequently, uncertainty, complexity, and potential dangers affect the desire to adopt the technology.
Only some people know what a blockchain is and how it may be used. According to Andoni et al., blockchain adoption is slowed because the technology is most commonly linked with cryptocurrencies, which are almost anonymous and are occasionally used for malware or criminal payments. Nevertheless, blockchain and all emerging technologies need adequate understanding. Lohmer and Lasch, on the other hand, talk about how there need to be more trained specialists. When big companies invest in more training or hiring, SMEs are normally still in the beginning stages—getting more first-hand information from early adopters, users, and people who already know what they think is very important to solve this problem.
Conclusion
Digital transformation is a significant change that will affect all parts of a business, including its suppliers, customers, employees, value chains, business processes, business models, company policies, understanding of leadership, and ways of working. So, the idea of digital transformation is becoming more critical to businesses. In this light, knowing what kind of transformation a company wants is essential for developing a proper digital transformation strategy.
Blockchain technology provides numerous benefits for organizations but also has significant application issues that must be addressed. Companies must first identify their blockchain needs analysis and plan for these scenarios. They must carefully monitor and deliver the application stages within the companies.
Ultimately, the digital revolution has unlocked a world of endless possibilities, and blockchain technology is leading this change. There are countless opportunities, and blockchain technology will undoubtedly be a key component of businesses’ strategies to maintain competitiveness in the digital era.
FAQs
1. How blockchain is changing digital marketing?
Blockchain is transforming digital marketing by offering a reliable system for storing and exchanging information, boosting the credibility of marketing materials, and opening up novel channels for reaching and interacting with consumers using incentive-based, decentralized networks.
2. What are 5 key components of a blockchain system?
A blockchain system’s key components are nodes, consensus mechanisms, cryptographic hash functions, digital signatures, and smart contracts.
3. How blockchain technology change digital identity?
By reducing reliance on trusted third parties and increasing individual data ownership, blockchain technology offers a decentralized and secure solution for managing digital identities. It also makes it possible for various services and platforms to verify users’ identities in a unified and configurable manner.
4. Can blockchain replace internet?
No, blockchain will not be able to replace the internet. It is a technology that runs on the internet’s infrastructure.
5. How blockchain is transforming businesses?
Blockchain is altering organizations by enabling secure, transparent, and decentralized systems for transactions, data sharing, and record-keeping, which can increase efficiency, cut costs, and create new business models and revenue sources.