Table of Contents
Introduction
Supply chain management has always been a difficult task for international businesses. The corporation has always spent much time and energy working out how to cut costs and address various inefficiencies.
Blockchain technology has encouraged businesses to look ahead. This technology could aid in the development of the supply chain. Analysts believe that blockchain technology can improve the current structure of the supply chain by increasing efficiency, trust, and transparency. In addition, many industry executives in the supply chain see blockchain technology as the way of the future.
PwC’s 2019 manufacturing sector survey found that over 24% are considering using blockchain for supply chain management. According to a study conducted by Deloitte in 2020, more than 55% of senior executives and practitioners ranked blockchain as their top priority.
Blockchain is a distributed ledger system that provides cheap and secure transaction settlement and transfer for its users. While blockchain is not a brand new internet infrastructure, it is highly novel in supply chain networks, representing the future of business.
Understanding the Basics of Blockchain Technology

Blockchain is a distributed digital ledger that can keep records of transactions securely and transparently. It was first presented in 2008 as Bitcoin’s underlying technology but has been used in many other contexts.
Blocks make up the blockchain and are connected in a chain using their respective dates. Each block includes a collection of transactions that nodes have confirmed, the participants in the network. A block cannot be changed or removed from the chain after it has been inserted.
Blockchain technology’s decentralized nature is an essential aspect of its design. Blockchain differs from traditional databases, which a single organization usually runs. Blockchain allows multiple parties to join the network and verify transactions. This means there is no central point of control and no single point of failure.
Security is another crucial aspect of blockchain technology. Once information is recorded on the blockchain, it can’t be changed without all parties’ agreement. This makes it extremely difficult for anyone, even hackers, to alter information stored on the blockchain.
Furthermore, there are several types of blockchains, such as public blockchains, private blockchains, and consortium blockchains. There is no need to ask permission to join a public blockchain; anyone can participate if they want to. Contrarily, private blockchains restrict access to only those specifically invited to join by the network’s administrator. Consortium blockchains are semi-private networks that require approval from several participants before you can join.
By eliminating the need for third parties or centralized authority, blockchain technology makes record-keeping for financial transactions simple, secure, and transparent. Because of its decentralized nature and high level of security, it is an excellent choice for use in supply chain management, where honesty and mutual respect between businesses are essential.
What is Supply Chain Management?

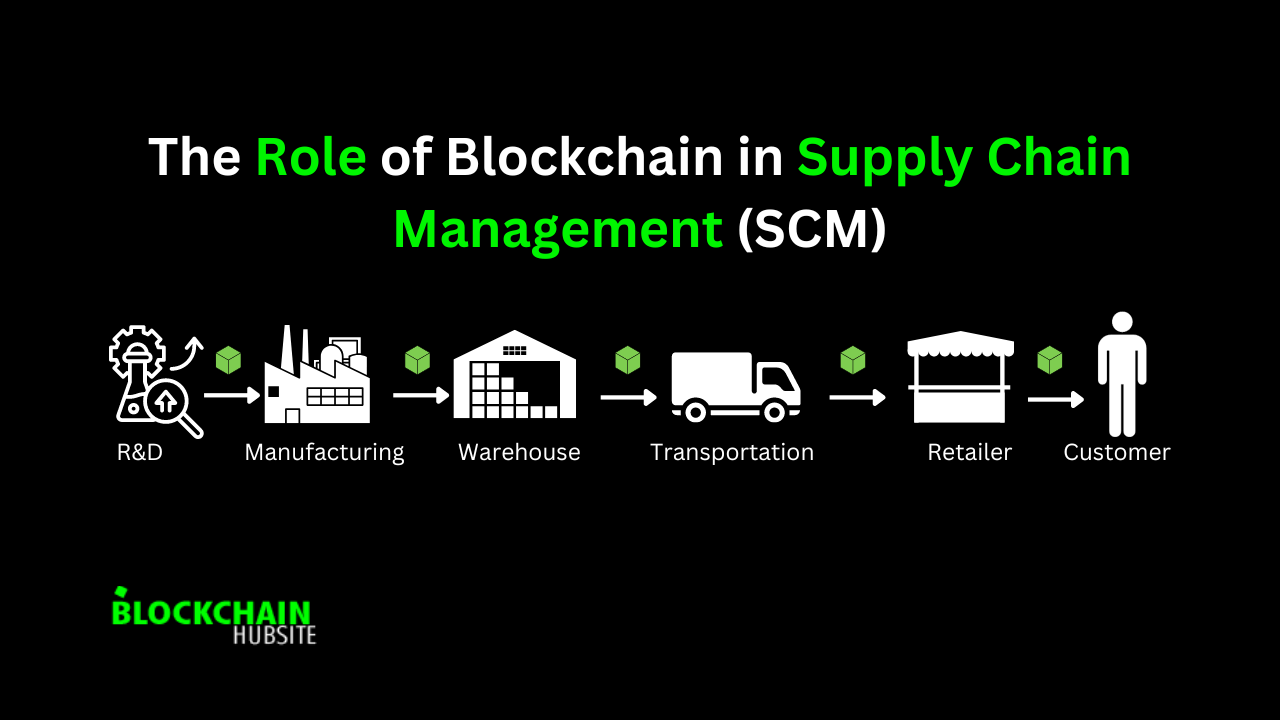
Supply chain management (SCM) is the term used to describe the entire “cradle-to-grave” or “cradle-to-cradle” networks of all businesses, people, modes of transportation, financial and information systems, consultants, and outside sources that take part in and contribute to a good or service from its very beginning to its very end.
SCM looks at all levels of clients and all levels of suppliers. All involved organizations work together in a cooperative relationship where risks, benefits, and information are shared, emphasizing the end user.
Cradle-to-grave is a term used to describe a product’s complete life cycle, from its initial conception and use of raw materials through its ultimate “death,” disposal, and environmental impact. In contrast, the Cradle to Cradle methodology emphasizes sustainability, recycling, and reuse; it is comparable to the circular economy but more environmentally friendly.
The initial stages of these design models may incorporate resources like forests, mines, oil fields, and farms. In contrast to cradle-to-cradle designs, which may be recycled, cradle-to-grave ones typically end up in landfills. Modern supply chains offer complete visibility and connectivity among network partners, regardless of the product life cycle model.
Difference between Supply Chain and Supply Chain Management
The term “supply chain” refers to the network of businesses and organizations producing and distributing a good or service. In contrast, “supply chain management” describes the coordination of these activities from the beginning to the point at which the final product is in the hands of the customer.
Blockchain: The missing link in effective supply chain management

Maersk and IBM collaborated to develop the TradeLens platform, which uses blockchain technology to enable complete visibility and transparency throughout the supply chain.
Through its compatibility with and enhancement of electronic data exchange (EDI) systems, the technology may also help other businesses save billions of dollars and cut down on inefficiencies. After the elimination of paper-based systems and the introduction of electronic document exchange between trading partners, this is the next logical stage in the supply chain’s development.
How Does the Blockchain Work in Supply Chain Management?

Blockchain technology has the potential to significantly improve supply chain management by boosting transparency, security, and efficiency. Here is how it works:
A blockchain is a secure and transparent digital ledger that keeps track of transactions. Each transaction gets verified by several people in the network, and once it has been approved, it is added to a group of transactions called a block. Each block is connected to the one before it, making a chain of blocks. This is why it is called a “blockchain.”
In supply chain management, the blockchain can track goods and their movements from origin to destination. Each transaction in the supply chain is recorded as a block in the blockchain. The block includes information like the date, time, location, and other essential data.
Since the blockchain is distributed, all participants in the chain can access the same data. Since more information is now available, organizations may address slowdowns and other inefficiencies in the supply chain.
Also, the blockchain can help ensure the supply chain data is secure and correct. Since each block is connected to the one before it, tampering with the data on the blockchain is extremely difficult. This makes the blockchain an ideal way to reduce the risk of theft, counterfeiting, and other types of corruption in the supply chain.
Lastly, the blockchain can make the payment process in the supply chain more efficient by making transfers faster and safer. Smart contracts, self-executing contracts in which the terms of the agreement between buyer and seller are directly encoded into lines of code, can automate payment processes, minimizing the need for intermediaries and lowering transaction costs.
Benefits of Implementing Blockchain in Supply Chain Management

There are several potential benefits of integrating blockchain technology into supply chain management.
1. Improved traceability, transparency, and trust
The primary feature of the blockchain is that it provides an immutable and transparent record of all supply chain transactions. As a result, products can be tracked more quickly from their point of production to their final destination, which increases transparency and decreases opportunities for fraud. This allows businesses to track their products better and closely monitor how things are going along the supply chain. This, in turn, can increase trust between partners in the supply chain.
2. Increased efficiency leads to speed
Blockchain technology can improve efficiency and save costs throughout the supply chain by automating several activities. As examples, we can think of payment automation, inventory management, and logistical streamlining. It also makes room for another important part: the need for speed.
3. Reduced Costs
Blockchain technology can help reduce costs across the supply chain by eliminating intermediaries and cutting administrative costs. This includes everything from conceptualization and planning to production, distribution, and product return.
For example, the automotive business can save money by lowering inventory tracking costs. Checking product availability and manually updating records are just two examples of the current manual processes involved in inventory tracking. By implementing blockchain technology, businesses may streamline and simplify these operations.
The blockchain could also be used to store and share data safely throughout the whole lifecycle of a product. This means everyone involved in the supply chain, from producers to retailers, has instantaneous access to the same information. This can assist in minimizing costs associated with manual data entry and inaccuracies while improving communication among all parties involved.
In addition, a considerable quantity of paperwork has been reduced from the entire supply chain. More than just a secure platform for tracking progress throughout the design process and ensuring that modifications are logged precisely, blockchain can also assist in reducing product development expenses. This reduces the chance of mistakes and delays during development and speeds up the time-to-market (TTM).
4. Immutability provides enhanced security
The distributed ledger and cryptographic methods used by blockchain ensure its extreme security. One of the primary benefits of blockchain technology is its immutability. Distributed ledgers and cryptography provide for the permanent security and immutability of data recorded on a blockchain. This makes it extremely difficult for bad actors to change the blockchain or its transaction history. Since all data is immutable and can be easily traced back to its source, immutability also improves traceability throughout a supply chain. All along the supply chain, this helps build confidence and transparency between all involved parties.
5. Improved Customer Service
With the help of blockchain technology, supply chain management may be streamlined, ultimately benefiting the client. Because of blockchain’s immutability, consumers can see where their purchases came from and how far they traveled throughout the supply chain. This helps customers trust companies because they can see exactly where their product is and know it is accurate and has been sourced responsibly.
In this decade, sustainability has become increasingly important to consumers and businesses. Trust and the ability to make sustainable choices that affect the world and the lives of the people working on the product are very satisfying and lead to a great customer experience and happiness.
Disadvantages of Blockchain in Supply Chain Management

- Permissioned blockchains
Due to the potentially sensitive nature of supply chain data, permissioned blockchains (blockchains that require special access to view or participate in) are often preferred. The blockchain in a permission system is minor, and its participants are more likely to know each other, making it easier for them to conspire to alter a block.
- Human factor
While it’s beneficial for all parties involved in a supply chain to be aware that data entered into a blockchain cannot be altered once it has been established, human mistakes or malicious activity may still occur while entering the first data. Therefore, the data stored in a blockchain may need to be more accurate or even fraudulent. For example, a bad actor could fill a container with rocks yet record on the blockchain that the container was filled with auto parts.
While blockchain technology may make it easier to determine where in the supply chain rocks were secretly placed, it cannot stop false data from being added to the ledger in the first place. Blockchain technology keeps wrong information from being added to the chain. Instead, it lets every user on the chain confirm that the data on the chain hasn’t changed since a particular point in time. Due to the blockchain’s inherent immutability, it becomes troublesome when malicious actors put false information into the network.
Accenture has made a prototype that would let the people in charge of permissioned blockchains change past transactions in rare cases to fix human mistakes. However, some blockchain experts have criticized such approaches, saying that removing immutability defeats the purpose of using blockchain over a traditional database.
Due to the need for validation on a distributed network of computers or servers, blockchain systems are much slower at processing transactions than conventional databases. A permissionless feature of a blockchain system may also be expensive due to the massive number of supply chain transactions. Transaction fees would be required for the miner nodes‘ labor to construct the blocks. The use of blockchain technology must be carefully considered with scalability in mind, as certain supply chains process millions of transactions every day.
- Upfront costs
Initial blockchain system implementation costs may be high. Hiring blockchain developers can be expensive since their specialized knowledge makes them more in demand than traditional developers. There may be hidden expenses, such as those associated with planning, acquiring licenses, and maintaining the system.
Use Cases for Blockchain in Supply Chain Management
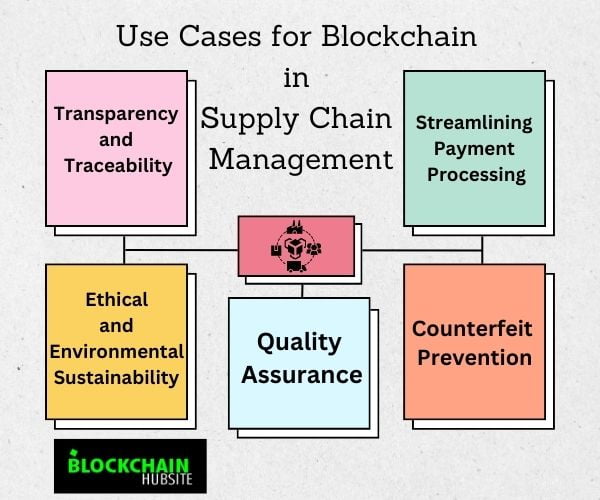
There are many different ways that blockchain technology could be used in supply chain management. Some of the more interesting potential uses are listed below. Most of the use cases and benefits of tracking something start with traceability.
1. Transparency and Traceability
Maintaining network visibility is a significant challenge for executives in supply chain management. Blockchain technology’s safe and transparent supply-chain tracking solutions can help with this problem. This can boost productivity, safety, and customer satisfaction across the retail, wholesale, and retail value chains and ultimately benefit consumers.
2. Ethical and Environmental Sustainability
As environmental, social, and governance (ESG) considerations rise, the blockchain will track carbon emissions and other environmental impacts along the supply chain to promote ecological sustainability. This information can then be used to find places to improve and reduce the environmental impact.
Businesses can use blockchain technology to verify that their supplies come from legitimate sources. By tracking goods to their initial Inception, companies can spot and report supply chain problems like child or slave labor, low salaries, or unsafe working conditions.
3. Quality Assurance
Blockchain technology may monitor and maintain product quality along the supply chain. Companies can monitor and ensure they meet regulatory standards by capturing data on the blockchain at each manufacturing phase.
4. Counterfeit Prevention
Counterfeiting is a significant issue in many sectors but is particularly problematic for the luxury goods and pharmaceutical industries. By maintaining an immutable record of product ownership and authenticity, blockchain technology can aid in the fight against counterfeiting.
5. Streamlining Payment Processing
Payment processing in supply chains is another area where blockchain technology can improve efficiency. Smart contracts allow for the automation of payments based on fulfilling certain conditions, such as passing a quality check or a delivery certification.
These are just some of the many applications of blockchain technology that may be found in logistics management. There will undoubtedly be increasingly creative applications of this technology as time goes on.
From Traceability to Transparency: How Big Companies are Revolutionizing Supply Chain Management with Blockchain
Supply chain efficiency can be significantly enhanced by implementing blockchain technology, which is already being done by many industry leaders such as FedEx, Maersk, UPS, Walmart, Ford, BMW, and Tesla.
- Walmart built a digital food supply ecosystem and used blockchain technology to automate the whole food supply chain, speed up openness, and reduce paper waste.
- Maersk and IBM have collaborated on a global cargo shipping service that uses blockchain technology to boost productivity.
- FedEx used blockchain technology for inventory control and shipping monitoring.
- UPS and Inception built a blockchain-based platform to optimize the logistics of UPS’s merchant partners. UPS is also working on plans to implement a blockchain system for tracking and storing package information such as delivery address, location, mode of transit, and more.
- Ford used a blockchain to monitor cobalt flow for electric vehicle battery production, allowing them complete visibility into manufacturing.
- BMW has adopted blockchain technology to monitor the flow of vehicle headlights, along with all other raw materials and components, and plans to expand the system to incorporate additional automobile parts suppliers.
- Tesla effectively implemented the technology to streamline the inbound supply chain to the Shanghai, China, production plant.
The Future of Blockchain-based Supply Chain?

Customers want a blockchain-based supply chain to verify the legality and sustainability of a product’s production and origins.
Applying blockchain technology to supply chain management could solve problems with current supply networks, such as the time and effort required to complete paperwork. More visibility and transparency in the supply chain can be achieved using a distributed, immutable ledger to record all transactions and businesses’ digitalization of physical assets.
Since a high skill level is needed to realize the benefits, blockchain implementation in the supply chain has yet to gain widespread acceptance. Because blockchain technology is so new, it is regulated differently in several countries, which might disrupt existing supply chains. Blockchain-based solutions will replace traditional supply chain processes and networks, but this shift will take time.
Conclusion
In conclusion, blockchain technology can change supply chain management by making it more secure, efficient, and open. It could eliminate the need for mediators and lower costs for companies. Blockchain’s decentralized design makes it difficult to compromise the system through fraudulent means like hacking. But there are still problems that need to be resolved. Even though there are problems, the possible benefits of blockchain in supply chain management make it a promising technology for the future of business operations. As the technology continues to develop and more people use it, we can expect to see even more improvements in supply chain management made possible by blockchain.
FAQs
1. How does blockchain technology impact supply chain performance?
Blockchain technology can improve supply chain performance by providing transparency, traceability, and security to supply chain operations, reducing costs, and increasing efficiency.
2. Which company uses blockchain in the supply chain?
Many companies, including Walmart, IBM, Maersk, and UPS, use blockchain in their supply chain operations.
3. What is the weakness of blockchain in the supply chain?
The weaknesses of blockchain in the supply chain include scalability, interoperability, and regulatory challenges.
4. What are the three problems of blockchain?
The three problems of blockchain are scalability, interoperability, and regulatory challenges.
5. What is meant by blockchain in logistics?
Blockchain in logistics refers to using blockchain technology to improve logistics operations, such as tracking and tracing goods, verifying authenticity, and reducing fraud and errors.
6. Which blockchain is most favorable for supply chain and logistics?
The blockchain most favorable for supply chain and logistics is currently considered the Ethereum blockchain.