Table of Contents
Blockchain technology has been around us for the last few years and is still gaining popularity daily. Even though everyone has different feelings about this technology, no one can deny its importance to the global industrial landscape. This technology first came into the public eye through the most popular cryptocurrency, bitcoin. Sadly, compared to other cryptocurrencies, this specific cryptocurrency has become more overrated and unstable.
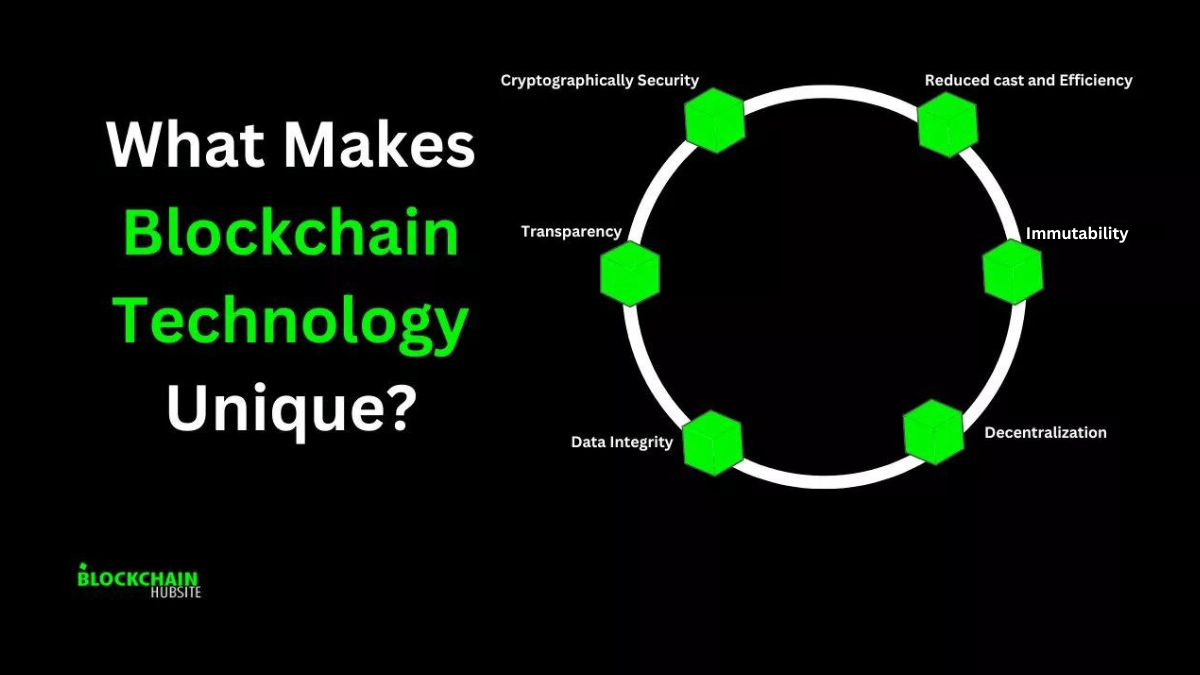
In this blog post, we will discuss in detail about key features of blockchain Decentralization, Transparency, Immutability, Data Integrity, Cryptographically security, and Reduced cost and efficiency that make this technology unique.
6 Key Features That Makes Blockchain Unique

Blockchain technology serves as a backup network for cryptocurrencies and provides a lot more than this. So let’s dive deep into its key features.
1. Decentralization
Decentralization is one of the main features of blockchain that makes this technology unique. Decentralization in the blockchain is the transfer of control and dominancy to a distributed network from a centralized governing body. It helps restore equality and justice between network participants by eliminating interference and control from any group, individual, or government.
Blockchains are made up of individual blocks and verified transaction data on each block happens over a given period. Since the blocks are added continually and uninterruptedly to build the blockchain, the data verification and confirmation in each block is the responsibility of the global community of decentralized participants operating Computing nodes.
The main aim behind the launch of Web3 was to eliminate the need for large tech companies that play the role of intermediaries by providing users complete control and ownership of their data.
Many believe their network has no public leader; however, decentralization only partially eliminates leadership.
1.1 How Does Decentralization Work?
The prominent highlights of blockchain are the requirement for consensus between the network users and for conducting transactions independently without the interruption of centralized authority. As the transaction on the blockchain network can only be done after the verification from all the network users, one may ask, “is it truly decentralized.” To understand the concept of decentralization effectively, let’s dive deep into how transactions take place on the blockchain.
In the case of the Bitcoin blockchain network, the new transactions do not move directly on the blockchain. A transaction must undergo a verification process before adding to a block. The question arises, “is there any kind of authority for the validation”? The decision-making and power in the case of a decentralized blockchain are not in the control of any individual or group. These are evenly distributed between the participants of the network to avoid unfairness.
In general, the authenticity of each new block is verified through different connected yet separated nodes. It shows how secure the blockchain is because one has to access multiple blocks to alter any specific portion of the blockchain.
1.2 What is the Importance of Decentralization in Blockchain?
- The popularity of blockchain is closely related to decentralization. Decentralization helps to ensure that the network is not controlled by a group, a single entity, or even by the government. Instead, the power is distributed systematically among the participants to avoid meddling with the transaction. It also helps in preventing any insider trading in the blockchain.
- The miners and investors can access all the data in the blockchain in real-time, which helps prevent data loss and incorrect data. It behaves more like google docs, where we not only share data with various people but can also edit it simultaneously.
- For the perfect usage of resources, decentralization ensures that the whole blockchain network is equally distributed between various nodes.
- Because of decentralization, no intermediaries are required for the transaction process, which makes blockchain transactions faster than bank transactions.
2. Transparency
Transparency is one of the main features of blockchain technology. Transparency plays a vital part to makes blockchain unique. The advancement in cryptography has made it much easier to validate the technology behind blockchain, which in turn increases the user’s confidence in the technology. But whether blockchain technology is transparent or more of an ideology arises. Let’s take a closer look at how transparent blockchain technology is.
2.1 Provably Fair
Bitcoin gaming sites are where blockchain technology indeed shows off its transparency. The provably fair games enable players to check the server seeds of the game to guarantee that the results they are receiving are accurate and fair, but the advantage is always in the hands of the house. Transparency is a comprehensive aspect of online gaming. Other casino sites and gaming platforms also use it to build trust between the website and its players.
2.2 Privacy
Privacy is one of the main elements people want to know about when discussing the transparency of blockchain technology. Technology cannot be transparent if there are unidentified users on the blockchain. Surprisingly individuals are much more open when interacting with technology because all the actions cannot be linked to a single identity. This helps blockchain to remain transparent.
The technology is gaining popularity because of its privacy while tracking and storing transactions on the network.
2.3 Fully Auditable & Valid Ledger Of Transactions
Besides the technology’s remarkable privacy, it also delivers unparallel transparency in the case of its fully auditable and valid ledger of transactions. As all the site transactions are unchangeable, no one can try to manipulate, change or erase the data once the network verifies it.
To make changes in the transaction, one has to change every other block in the system; this makes the transaction-changing process impossible in the blockchain. This automatic transparency is the main feature of a blockchain network and also helps reduce the need for checks and balances.
2.4 No single Entity Control
The blockchain’s decentralized network prevents the control and manipulation of a single entity in any way as blockchain technology is based on a peer-to-peer network, so regular users worldwide, known as miners, are responsible for verifying each transaction. By doing this, the platform remains incredibly transparent and ultimately reliable, encouraging more people to learn how to use blockchain technology.
2.5 Transparency in cybersecurity
It’s undeniable that blockchain is changing our view regarding cybersecurity. One of the many benefits blockchains provides to regular end users, security companies, and even governments in cybersecurity is transparency. We need to come across a technology that guarantees the legitimacy of attacks and makes them public simultaneously.
Blockchain provides security suppliers concrete data to support their claims of performance or efficiency, and users, when selecting a cybersecurity solution, will also be able to refer to this data.
3. Immutability

Immutability refers to unchangeability. It is one of the primary characteristics that make blockchain unique. Thanks to immutable transactions, no entity like a government or corporation can alter, modify or falsify the data stored on the network.
3.1 Understanding Blockchain Immutability
The immutability of the blockchain ledger is its ability to stay unaltered, unchanged, and permanent. A cryptographic principle or hash value is used to carry out each information block, such as facts or transaction details.
Now, each block generates independently for this hash value an alphanumeric string. Each block has a digital signature or a hash value not only for itself but also for the block before it. This, in turn, shows that in the past, the blocks are implacably tied together. Due to this feature of blockchain technology, no one can tamper with the system or change the data that has already been saved into the blocks.
3.2 How is Immutability Achieved?
The clarity of the cryptographic hashes concept is necessary to understand how to achieve immutability. The primary benefit of the hash is that it cannot be reverse-engineered, which is why it is more popular. The most widely used hash function is Secure Hash Algorithm 256(SHA-256).
Currently, the cryptographic creation task is no longer a difficult one. It’s all because modern programming languages offer a variety of hash functions. After using these hash functions, we must pass a set of bytes, returning a checksum signature. These functions always produce a string length of 64 characters, and no matter the input size, we will always get the fixed length of string, which is often known as a digital signature.
The digital signature indicates the exact data entered by the user. To identify the input data, the users cannot use these output strings as the hash cannot be reverse-engineered. From this, we get the immutability of the blockchain ledger. Each transaction in this system is validated with the help of a blockchain network. It contains blocks of information with timestamps inserted and is protected by a hashing process. It includes the hash of the last block and staying connected. This technique is vital in developing the chronological chain, which helps block linking.
Whenever we create a new hash for a block, the meta-data of the previous block is always included by hashing. As a result, the block and the chain are linked and become unbreakable. After that, once the block is added to the blockchain, no one can change or delete the block’s data. The reason is that whenever someone tries to make modifications, the change will be rejected by the next block as the hash of the block is no more valid.
3.3 Understanding the Challenges to Blockchain Immutability!
Indeed the entire blockchain system is undoubtedly reliable, but still, there are a few challenges that need to be solved. Let’s have a thorough understanding of these challenges.
51 Percent Attack
The potential threat for this mechanism is the possible 51 Percent attack, where an attacker can get considerable power over the network compared to other members. No single entity can control the network in blockchain due to decentralization. However, by the production of hashing power, the miners can still ruin the immutability of the blockchain system.
Due to the rapid growth of the mining market and the availability of renting mining capacity, carrying out such attacks is no longer difficult. As a result, the attackers can easily change the initial transaction data considered immutable. The hackers can reverse the high transaction data by using this facility and secure profit by spending money again.
Quantum Computing

Quantum computing is another serious challenge for blockchain technology. Because of it, the immutable nature of blockchain is in danger. Several research studies show that quantum computing can reverse-engineer the blockchain network’s public key, which then can be used to find the private key for hacking the system. In this area, it is undoubtedly a serious challenge; almost 50 percent of blockchain can be affected by it.
3.4 Overcoming the Challenges
It is crucial in this regard to overcome the challenges mentioned above. Experts’ studies show that we can deal with 51 percent of attacks effectively by implementing consensus algorithms like proof-of-stake or delegated proof-of-stake and creating a robust protocol. Instead of renting out the processing challenge, it can be expensive to stake many tokens on a network. However, it still needs to be determined whether we can entirely rely on these solutions to face a threat like this.
To deal with the quantum computing challenge rightly, we must include quantum cryptography in the blockchain foundation. The creation of blockchain architecture with quantum particles in the future will enable us to record all history more securely. The solutions for these problems are far in the future. To overcome the challenges, we must stay cautious while implementing blockchain.
3.5 Benefits of Immutable Ledger in Blockchain

Ensures Authenticity and High Quality
Blockchain’s immutability is very well known for its ability to provide users with high security and traceability. These features play a vital part in dealing with the fraudulent market effectively.
Well-known brands lose a large amount of money yearly due to counterfeit products, but the blockchain is the ground-breaking solution. Its mechanism works by registering various products on the blockchain system, where makers can easily give their clients all the information they need regarding the products’ authenticity, historical records, and former and current owners. The buyers can determine whether an item is genuine by tagging it on a blockchain.
Security is Tight in Blockchain
The blockchain’s immutable ledger is highly secure, as we already know that blockchain is a distributed ledger. It means no single entity can control it. Therefore it is nearly impossible for hackers to attack it at any time, as there are more than two servers or nodes managing the data. In addition, each operation performed on a digital ledger is encrypted with a unique hash code and can take place only with the permission of the majority of the nodes. This ensures a free and transparent data flow and protects it from being corrupted.
Readily Benefits Supply Chain Management
Another area where blockchain’s immutable ledger has proven to be extremely useful is supply chain management. A great deal of care is required throughout the process of exchanging goods. During the transportation of goods, there is a possibility of loss, theft, misplacing, or damage. Because of it, several logistics companies have already begun utilizing blockchain to take benefits from it.
On the other hand, before adopting blockchain into their mainstream, several businesses are currently testing it. Thanx to blockchain technology; quick data sharing between parties is possible. Most importantly, no matter how minor inconvenience is caused during shipment, it will be reported. In this context, a digital ledger is essential in improving the transparency and traceability of items in the supply chain.
Higher Level of Privacy
The risk factors like hacking, leaking, or personal threats are always involved in sharing or posting information online. We typically treat data as private and work to ensure that it cannot easily be hacked in this way. Since blockchain differs from the traditional database, its usage here is highly advantageous because it guarantees far better user privacy. Discovering any user’s information is challenging because the blockchain is anonymous, and each user is protected with encrypted codes. However, it should be remembered that the privacy level varies depending on the specific blockchain and security measures it has.
4. Data Integrity
Maintenance of the integrity of data by using cryptographic techniques like hashing and digital signatures is one of the key features that makes blockchain unique. With the help of these techniques, the data cannot be altered or tampered with once it is recorded on the blockchain without being detected.
4.1 How to Ensure Data Integrity With Blockchain
Users always believe in the safety and accuracy of their data. Thanks to its advanced security capabilities, blockchain technology provides this much-needed assurance of data integrity.
Data integrity, confidentiality, availability, security, efficiency, and user privacy are all ensured by the blockchain solution’s cryptography encryption, which defends against attackers, prevents fraud and manipulation, and minimizes the risks that data will be stolen or corrupted.
Two fundamental ways of ensuring data integrity are
- Taking action in advance to prevent data from being changed
- Taking action in the downstream process to identify and remove data changes.
4.2 How to prevent the modification of data
- Data encryption is one of the best ways to prevent data from modification. Data encryption ensures that it is secure and that only authorized users can access it.
- Digital signatures and authentication protocols can also be used to verify data integrity.
- Logging and auditing systems are best for monitoring data changes and detecting any suspicious activity.
- Finally, access control methods can be used to limit who can make changes to the data.
5. Cryptographically Security
Cryptography is one of the methods of internet security. Encryption is converting information into code, allowing only the intended recipient to access the data. Data that has been encrypted is protected from potential hackers, which are known as “adversaries” in the cryptography world.
5.1 The role of cryptography in blockchain security
Cryptography plays a vital role in ensuring the integrity and security of blockchain.
- In the blockchain, cryptography is used to secure transactions by encrypting the data stored on the network. This assures that the data cannot be tampered with or altered without the proper encryption key.
- Cryptography is also used to secure communication between nodes on a blockchain network and to validate the identity of users on the network. The most widely used encryption methods in blockchain are Hash functions, Public Key Cryptography, and Digital Signatures.
5.2 What Does Cryptography Bring to Blockchain?
Here’s what blockchain gains from cryptography.
Security
The security of the blockchain ledger is based on cryptography. On the blockchain, every transaction is stored using encrypted data. Using their public and private keys, every user can access their data and buy and sell cryptocurrencies securely.
Blockchains use cryptographic hashing to store root hashes that encode every transaction securely. An entirely different hash will be generated at the root hash if someone tries to alter any data in the blockchain. Other users can detect that the data is hacked by comparing that root hash to the root hash on their computer.
Scalability
Limitless transactions can be stored securely by using cryptographic hashing across the network. Blockchains can keep growing at scale because so many transactions can be combined into a single hash.
5.3 Reliability
Transactions cannot be reversed because of the irreversibility of cryptographic hashing as this procedure protects them from any hostile activity, so it guarantees that all users can rely on the accuracy of the digital ledger.
6. Reduced Cast And Efficiency

Blockchain technology can reduce costs in some circumstances by eliminating the need for intermediaries, automating processes, and increasing transparency and security.
Efficiency is the term used to describe how well blockchain technology can optimize and simplify processes, leading to quicker transaction times and improved overall performance. Because of digital signature and encryption, the system is very secure, making it efficient, protected, convenient, and tamper-proof.
Final Thoughts:
Blockchain technology is not just a temporary thing that fades away after a few days. Considering all its key features and applications, we can confidently assume that blockchain is here to stay. A whole other level of impact is created by its features on the web.
Despite many controversies raised by blockchain, people can still use the concept behind all of its advantages, and they can create a brighter and more promising future for everyone.
FAQs
1. What is an attractive feature of blockchain?
The decentralization of blockchain technology is one of its most attractive features. As a distributed ledger, blockchain is shared across a network of computers rather than controlled by a single entity.
2. What are the biggest advantages to blockchain?
The primary advantages of blockchain technology are decentralization, immutability, security, and transparency.
3. How is blockchain better than a database?
In several ways, blockchain is better than traditional databases. As blockchain is decentralized, no single entity can control it, making it more secure and less vulnerable to attack. Besides that, because blockchain is immutable, no one can change or remove the transaction once it is add on to the blockchain. Furthermore, because of the use of cryptography, blockchain is more secure, making it difficult for unauthorized parties to access or tamper with the data.
4. What problem does blockchain solve?
Blockchain solves the problem of trust in digital transactions by providing a secure, transparent, and tamper-proof method of storing and verifying data.
5. What is the most important part of the blockchain?
The most important part of the blockchain is the distributed ledger, which records all transactions. This ledger is maintained regularly by a network of computers known as nodes responsible for validating and verifying transactions.
6. How is blockchain used in real life?
Blockchain technology is used in many real-world applications, from financial services to healthcare, government, and supply chain management. Moreover, blockchain technology has the potential to facilitate the exchange of digital assets such as cryptocurrencies.