Table of Contents
Introduction
There has been a dramatic increase in the cost of cybersecurity over the past decade. And this trend will keep going. The cybersecurity industry was worth more than $170 million by 2020. It is projected to reach $400 billion by 2027. Despite this massive investment, cybercrime generated losses of $1 trillion in 2020 (1% of global GDP), and this number is expected to rise to $6 trillion by 2025.
Blockchain is likely the only technology capable of reducing cybercrime’s impact because of its improved data map, stronger authentication, and secure edge computing.
Blockchain technology offers promising solutions to numerous significant challenges in cyber security. Blockchain revolutionizes traditional business operations by providing a decentralized database for storing trustworthy ledgers and processing computations. Also, many people’s faith in centralized authorities (such as banks) has shifted to cryptography and other techniques.
The blockchain is a complicated system with many distinct components and applications. Although blockchain has several uses, some of its qualities are particularly helpful in cybersecurity.
This article will discuss blockchain technology’s increasing popularity in the cybersecurity industry and its advantages and potential drawbacks.
What is Blockchain?
A “blockchain” is a data structure used in some distributed ledgers. It stores and sends data in ” blocks ” packages linked in a digital “chain.” Blockchains use cryptographic and algorithmic techniques to record and synchronize data across a network in a way that cannot be altered once recorded.
Overview of Blockchain cyber security

Blockchain cybersecurity uses blockchain technology to protect digital systems from cyber threats and make them safer. Blockchain’s distributed ledger design makes it ideal for managing digital identities, storing transaction records, and ensuring data integrity.
Blockchain technology can make the Internet of Things (IoT) and other vital infrastructures more secure. Furthermore, blockchain can increase the safety of private communications by blocking third-party access to confidential messages. In general, blockchain might greatly improve cybersecurity and reduce the possibility of cyber assaults.
The Role of Blockchain in cyber security
Blockchain technology has the potential to improve cybersecurity greatly. Here are a few ways blockchain might help improve cybersecurity:
Decentralized Storage
Blockchain’s ability to store information in a distributed manner is one of its most important aspects. Since there is no centralized data storage facility, it is more difficult for hackers to gain access to and steal data. Data stored in a blockchain-based system can also be encrypted and protected in other ways.
Security in the Internet of Things (IoT)
IoT devices are susceptible to cyber assaults because of their low processing power and insufficient protection. Blockchain technology can offer a safe and decentralized method of managing the Internet of Things by creating an immutable record of all interactions between devices. As a result, cyber assaults can be avoided, and the safety of the IoT ecosystem can be boosted.
Adding Security to Private Messaging

Traditional messaging services are susceptible to hackers and data breaches. When using a blockchain-based messaging service, users’ messages and associated data can be encrypted end-to-end, among other security features.
Reducing the Threat of Cyber-attacks to Human Safety
Blockchain can be used to protect vital infrastructures like energy networks, transportation networks, and healthcare facilities against cyber threats, making the world a safer place for people to live. Using blockchain to protect these networks will lessen the likelihood of cyberattacks that could endanger people’s lives.
Verification of Cyber-Physical Systems
Cyber-physical systems are those in which digital and physical components interact. Smart cities, self-driving cars, and factory automation are examples. Blockchain technology can be used to validate these systems’ authenticity and make sure they’re performing as expected. This can help stop cyber attacks resulting in real-world harm or damage.
Benefits of Blockchain Cyber Security
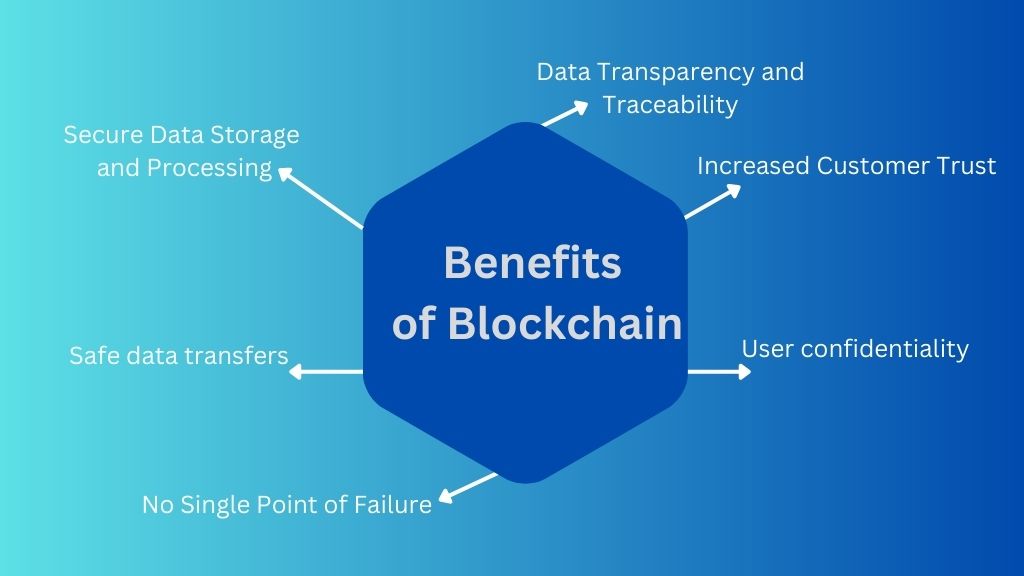
User confidentiality
Users are verified through the use of public key cryptography, which ensures that their identities will stay hidden at all times.
Secure Data Storage and Processing
Blockchain data is safe because it cannot be changed afterward. With its high level of privacy, it is perfect for storing sensitive data concerning security incidents like hacks and breaches.
Safe data transfers
Blockchain facilitates the instant and safe exchange of data and money. It includes elements such as smart contracts, which enable the automatic execution of agreements between parties throughout a transfer.
No Single Point of Failure
Even if a single node in the blockchain is compromised, the integrity of the network as a whole will remain unaffected. The system will continue functioning normally despite DDoS attacks because of the multiple ledger copies.
Data Transparency and Traceability
Every transaction made on a blockchain is digitally signed and timestamped, allowing network users to track accounts and trace transaction history easily. Due to the immutability of blockchain records, managers can more easily control access to private information. Without the need for manual updates or other tracking systems, everyone can see when and who made changes to data on a blockchain.
Increased Customer Trust
Blockchain’s data privacy and transparency help firms build customer confidence. The data owners can be given complete control over their information and have the power to determine who can access it and at what times.
Challenges of Blockchain Cyber Security

Scalability Issues
Blockchain networks have many restrictions, including the capacity of blocks and the number of transactions handled per second. Consequently, it would help if you verified the scalability of a blockchain platform before deciding to use it as the foundation for your solution.
These limitations are currently set at 1 megabyte (MB) of data and up to 7 transactions per second (TPS) for the Bitcoin network. The maximum rate blocks can be generated on the Ethereum network is between 7 and 15 TPS. However, other networks’ transaction capacity is said to be significantly higher. For example, Ontology thinks it can reach 4,000 to 12,000 TPS, based on the environment, while lab tests show that the Futurepia network can reach up to 300,000 TPS.
Reliance on private keys, often long sequences of random numbers created by a wallet’s software, are essential to blockchains. In contrast to user passwords, private keys used to communicate with the blockchain cannot be recovered. If a user loses their private key, the information it was used to encrypt is likely unrecoverable.
Adaptability Issues
While blockchain technology can be implemented in practically any industry, firms may need help integrating it. For example, incorporating this technology into supply chain management is difficult because it could take a long time to re-implement the supply chain logic using a blockchain. Blockchain applications may also need to replace all current systems, so companies should consider this before implementing blockchain technology.
Possibility of Cyberattacks
Blockchain technology dramatically minimizes the possibility of suspicious intervention, but it doesn’t eliminate all cyber threats. There are vulnerabilities in the blockchain, such as in the coding, the consensus methods (51% attack), and the communication between nodes (eclipse attack). If malicious actors can exploit even one of these flaws, the entire system’s safety could be in danger.
High Operation and Customization Costs
A blockchain requires a lot of computational power and storage space. In comparison to traditional, non-blockchain-based systems, this could increase marginal costs.
Education About Blockchain Technology
There need to be more trained blockchain developers and cryptography specialists, despite the growing need for blockchain solutions. Blockchain development requires a wide range of skills and a deep understanding of many technologies, programming languages, and tools, including tools for testing blockchain security.
Lack of Governance
There currently need to be more international regulations governing the operation and application of distributed ledger technology in general. Many countries, like the US and Malta, already have or are working on cryptocurrency rules. In the United States, several states have passed laws and built frameworks for using blockchain technology and smart contracts in legal and commercial contexts.
These are the biggest blockchain negatives to consider before implementing this technology to increase the cybersecurity of your product. But the ultimate compilation of possible downsides will rely on the industry you work in and the other problems you want to solve with the help of the blockchain.
Blockchain Use Cases for Cybersecurity

Despite being somewhat unbreakable, blockchain has developed into one of the most secure ways to conduct transactions in digital networks. The technology has been praised for ensuring information integrity in the way it was intended and constructed. It can be beneficial to many industries if used properly.
Blockchain technology can be used in a wide variety of applications. Utilizing its integrity assurance to create cybersecurity solutions for numerous other technologies would be one of the finest uses.
Here are a few examples of how blockchain could be used in the future to improve cybersecurity:
1. Security for Private Messaging
More and more individuals are using social media as the internet turns the world into a small, interconnected village. The number of social media sites is also growing. With the rise of conversational commerce, new social apps appear with each new day. These interactions result in the collection of a significant amount of metadata. Most social media platform users safeguard their services and data with insecure, unreliable passwords.
Most messaging companies are coming around to the idea of using the blockchain instead of their present end-to-end encryption to secure customer data. A standardized security protocol can be established using blockchain technology. Blockchain can be utilized to create a single API architecture for providing cross-messenger communication capabilities.
Numerous recent attacks have been carried out against social media sites like Twitter and Facebook. Millions of accounts were compromised due to these assaults, and user information was in the wrong hands. If properly integrated into these communications systems, blockchain technologies protect against such cyberattacks in the future.
2. IoT Security
Hackers are increasingly using edge devices like routers and thermostats to access larger networks. Due to the current obsession with artificial intelligence (AI), it is now simpler for hackers to gain access to core systems like home automation through edge devices like “smart” switches. The majority of these IoT gadgets have questionable security features.
In this situation, blockchain can be used to safeguard such large-scale systems or devices by decentralizing the management of such large-scale systems or devices. The method will enable the device to make security decisions independently. By identifying and responding to questionable commands from unknown networks, edge devices become more secure by not relying on the central admin or authority.
Typically, when a device’s central administration is breached, the devices and systems are immediately in complete control of the hacker. By decentralizing such device authority mechanisms, blockchain makes such attacks more difficult to carry out (if even conceivable).
3. Protecting DNS and DDoS
When users of a network resource, server, or website are prevented from accessing or using the help in question, this is known as a Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) assault. These assaults disable or delay the resource systems.
However, hackers who aim to break into the connection between an IP address and the name of a website will find a fully functional Domain Name System (DNS) to be an easy target due to its centralized nature. This attack can make a website unusable, steal sensitive information, or even lead users to other malicious domains.
By decentralizing the DNS entries, blockchain may be utilized to reduce these kinds of attacks. Blockchain would have eliminated the single points of vulnerability that hackers exploited using decentralized solutions.
4. Decentralizing Medium Storage
Theft and hacking of business data are increasingly causing organizations to express concern. The majority of businesses still use the centralized storage method. A hacker must target just one weak spot in these systems to access all the data. In the event of such an assault, the attacker gains access to sensitive information, such as a company’s financial records.
Sensitive data may be protected by employing blockchain to provide decentralized data storage. Hackers would find it more difficult, if not impossible, to access data storage systems using this mitigating technique. Many storage service providers are investigating how blockchain can safeguard data against hackers. The Apollo Currency Team is a prime instance of a company that has integrated blockchain technology into its infrastructure (the Apollo Data Cloud).
5. Computer Software’s Provenance
Blockchain can be used to track and prove the authenticity of software from the time it is created until it is put into use. This can prevent malware and other online threats that might be brought about by unauthorized or harmful software.
6. Verification of Cyber-Physical Infrastructures
Blockchain can validate and guarantee cyber-physical infrastructures’ reliability, including transportation and electricity grids. This way, harmful cyberattacks that could impair essential services or even cause physical injury can be avoided.
7. Protecting Data Transfer
Blockchain can protect data transfer by encrypting and storing data in a decentralized, unchangeable ledger. This can protect against sensitive data breaches and illegal access.
8. Reduce the Risk to Human Safety Caused by Cyber Assaults
By providing real-time monitoring and reaction to possible threats, blockchain can be utilized to reduce the risk to human safety caused by cyber assaults. This can help avoid mishaps or other negative outcomes brought on by cyberattacks.
9. Authenticating Edge Devices
Blockchain can provide a decentralized authentication mechanism for securing edge devices like the Internet of Things (IoT). This can help stop these gadgets from falling into the wrong hands and being used in cyber attacks.
10. Improved secrecy, Integrity, and Authenticity
By offering a decentralized, tamper-proof ledger, blockchain may be utilized to increase the secrecy, integrity, and authenticity of data. This can assist in confirming the integrity of the data and prevent unauthorized changes or access.
11. Boosting or even Replacing PKI
By offering a decentralized, secure, and tamper-proof framework for storing and managing digital certificates and keys, blockchain can enhance or even replace established Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) systems.
12. DDoS Attacks Reduction
By offering a decentralized, robust network that can survive attacks and retain availability even in the face of sustained traffic spikes, blockchain can be utilized to lessen the impact of Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks.
13. Enabling Multi-Signature Authentication Model
Blockchain can allow multi-signature authentication models, in which several parties must first authenticate a transaction or action before it can be carried out. Requiring agreement from numerous parties can aid in preventing fraud and illegal transactions.
Concluding Remarks
Blockchain technology has completely changed the cybersecurity landscape by offering a safe and decentralized platform for storing sensitive data. It prevents cyberattacks due to its decentralized security, immutability, and transparency. Since safety is becoming more important in today’s digital world, it’s not surprising that blockchain technology is being used increasingly in this area. Businesses and people can use this technology to ensure their private information stays safe and can’t be changed.
FAQs
1.How is blockchain a new cyber security weapon?
Blockchain can be a new weapon for cyber security because it can be used to store and verify information safely and decently. The distributed ledger mechanism of the technology makes it impossible for hackers to compromise the integrity of data or change it without notice.
2. Why is blockchain the future of computer security?
Blockchain is regarded as the future of cybersecurity because of its ability to generate secure and immutable transaction records, making it harder for hackers to tamper with data. Because the technology is decentralized, there is no need for a central authority. This lowers the risk of a single point of failure.
3. How are cyber security and blockchain different?
Cybersecurity secures systems, networks, and data from digital threats, theft, and damage. On the other hand, blockchain is a technology that lets you store and verify data safely and decently. While cybersecurity works to protect data and prevent digital attacks, blockchain provides a secure means for storing and verifying data, making it harder for hackers to jeopardize the information’s integrity.
4. Why is cyber security important for cryptocurrency?
Cybersecurity is essential for digital currencies because they can be attacked online, and a successful attack can lead to the loss of funds or make transactions less trustworthy.
5. How is the security of a blockchain different from the tradational security?
Blockchain security differs from traditional security because it protects data and transactions with cryptographic algorithms and a decentralized, distributed network. On the other hand, traditional security frequently uses centralized servers and access controls to safeguard data. Additionally, while conventional security relies on identity and authorization, blockchain technology uses a consensus process to confirm transactions and stop unauthorized alterations.